What is Pay Parity?
Pay parity refers to the proposition of providing equitable pay or compensation to individuals with equal job roles and delivering work of equal value, irrespective of their caste, race, gender, or other personal protected traits.
It is also known as ‘pay equity’ or ‘equal pay’. It aims to eradicate the pay gaps that pertain due to stereotypical mental shortcuts or cultural conditioning of people in the workplace.
It ensures equal pay to individuals with equal potential, working conditions, efforts, and responsibilities. In addition, it mends the gender pay gap which not only exploits the skills of individuals but also degrades their morale ultimately affecting their efficiency.
What is Gender Pay Parity?
Gender pay parity refers to the principle that ensures equality in payment for both men and women workers with equal work value or the same job responsibilities in similar work conditions.
It aims to promote gender equality as well as a fair pay concept for every individual irrespective of their gender whether male or female for similar nature of work conducted. This as a result robust the efficiency of employees specifically the women employees as well as other female to embrace education and employment opportunities.
To achieve Gender pay parity the government, organizations, and other exponents have implied various legislations or strategies which include:
- Pay Transparency
- Pay Audit
- Education and awareness regarding the gender pay gap and its consequences
- Policies that are framed to enhance employee-centric approaches and more.
What causes the Gender Wage Gap Between Men and Women workers?
There are some major causes that stimulate the gender wage gap between men and women employees which include:
➔ Stereotypical Credence
One of the crucial reasons that contribute to the gender pay gap is the ingrained stereotypical beliefs that are rooted in the cognitive memory of people. It not only puts diversified thoughts on hold but also limits an individual to accept optimistic facts hence contributing to initiating gender pay gaps.
➔ Ingrained Cultural Conditioning
The ingrained cultural beliefs of evaluating women as being less productive than men becomes a vital factor for the enhancement of gender pay gaps as well as disrupting the workforce balance in companies.
➔ Unconscious Bias
Unconscious biases are unintentional cognitive biases that are consequences of stereotypical axioms. These kinds of biases take the form of discrimination and are perceived to be an undisputable natural phenomenon blinding the mental acuity of employers or managers. Hence it results in conferring lower wages to women employees.
➔ Occupational Segregation
Occupational segregation denotes the difference in assigning job roles due to the pre-assumed patriarchal perception of talent management as per gender biases.
For example – Hiring male employees for fields like engineering, technology, and finance whereas considering women for administration, teaching, nursing job and etc.
➔ Lack of pay transparency
Another element that contributes to the gender pay gap is the lack of pay transparency which makes the gender gaps unnoticed hence surging the scope of disparities to persist.
➔ Void Penalties
Void penalties include parental leave or motherhood penalties that are a form of pay compromise due to maternity leave time off, reduced work hours due to caretaking responsibilities, biases that consider mothers as less competent, and more.
➔ Scattered opportunity access
Due to differences in access to education, the persistence of pay gaps becomes more vivid in society hence enhancing gender pay issues.
What are the causes of the Global Pay Gap?
The pay gap can be the consequence of various other factors that are globally dominant and have significant impacts some of which are as follows:
➔ Global gender gap
The global gender gap includes discrimination against women employees, black women, working mothers, and more.
As per the World Economic Forum(WEF) global gender gap report 2023, India has moved up eight places to rank 127 out of 146 countries in terms of gender parity. This still needs improvement to enhance the economy by encouraging the economic participation of the women’s labour force in the labor market.
➔ Systemic Discrimination
Systemic discrimination refers to the ingrained structures of society that go beyond the individual act of prejudice and is embedded in politics, norms, social norms, and regulations.
It includes age discrimination, discrimination based on ethnicity, race, caste, sexual orientation, disability, economic inequalities, gender stereotypes, patriarchal cognitive beliefs, and more.
➔ Societal Discrimination
Societal discrimination is the entrenched institution of society’s prejudice blinded by stereotypical, autocratic, and imperial values which affect and contribute to the global pay gap.
For example- working men are not expected for unpaid work which includes the burden of house chores, caregiving responsibilities, and more where as women are expected to take care of the entire house responsibilities which interrupts their career progression. Hence this determines a cause for the pay gap.
➔ Economic & Political Constraints
Economic and political constraints are pivotal in the enhancement of the global pay gap. The inequities between working men and women like health, occupation segregation, higher education access, gender-based violence and harassment by political leaders, and other gender inequality including discriminatory labor laws and practices, etc.
➔ Mitigation & Remittances
When people from less developed countries move to other developed places for better job opportunities and growth that creates a global pay gap.
Also Read:
How do you achieve pay parity?
There are various ways through which you could achieve pay parity. A few of these are discussed below:
➔ Addressing Structural and Systemic issues
It can be achieved by:
- Auditing, which will give an insight into the disparities pertaining to companies.
- Regular evaluation of internal policies to ensure equal pay for the same work to individuals with the same job role and equal pay range.
- Addressing complaints or grievances by women workforce against unfair promotion practices, faulty performance compensation policies, and related stuff.
➔ Conduct a pay audit
Conducting a pay audit can help evaluate:
- Uncover pay issues
- Can help assess inequities
- The average difference between men and women workers
- The wage gap differences
➔ Create a compensation framework
- Establish pay bands and salary ranges
- To protect the rights of workers with intersectional identities( overlapping and interconnected nature of various social categories).
- Create, review, and revise compensation practices as well as policies
- To provide equal access, benefits, and dollar earned by (both men and women ) employees on account of their abilities and skills and not due to systemic cognitive thoughts.
➔ Constructing Equitable workplaces
- By training and educating employers, managers, HR leaders ( as they are uniquely positioned to implement pay parity in the organization), and other employees about unconscious biases, discrimination, etc.
- Aware of the policies of the organization and the rules associated with the framed regulations to the company’s workforce as well as employers.
- Establish pay transparency by sharing salary ranges for different posts. This helps them determine how their salary is evaluated.
- Monitor and evaluate the measures implemented to eliminate disparities, the equal remuneration act, and other persisting.
Difference between Unequal Pay VS Gender Pay Gap

Who is most impacted by inequity in pay parity?
Inequity in pay parity or unequal pay for the same work assigned significantly impacts:
- Positive Workplace health and transit it into the adverse surrounding
- Hiring and talent acquisition
- Retention of employees and elevates staff turnover
- Navigate bad fame for the organization
- Legal risks that hamper the reputation of the company
- Employee morale and satisfaction take a toss
- Individuals ( mostly women employees) financial stability degrades
- The financial health of the organization.
- Productivity and efficiency of employees deteriorate
- Limits career succession and hampers the overall development of the company.
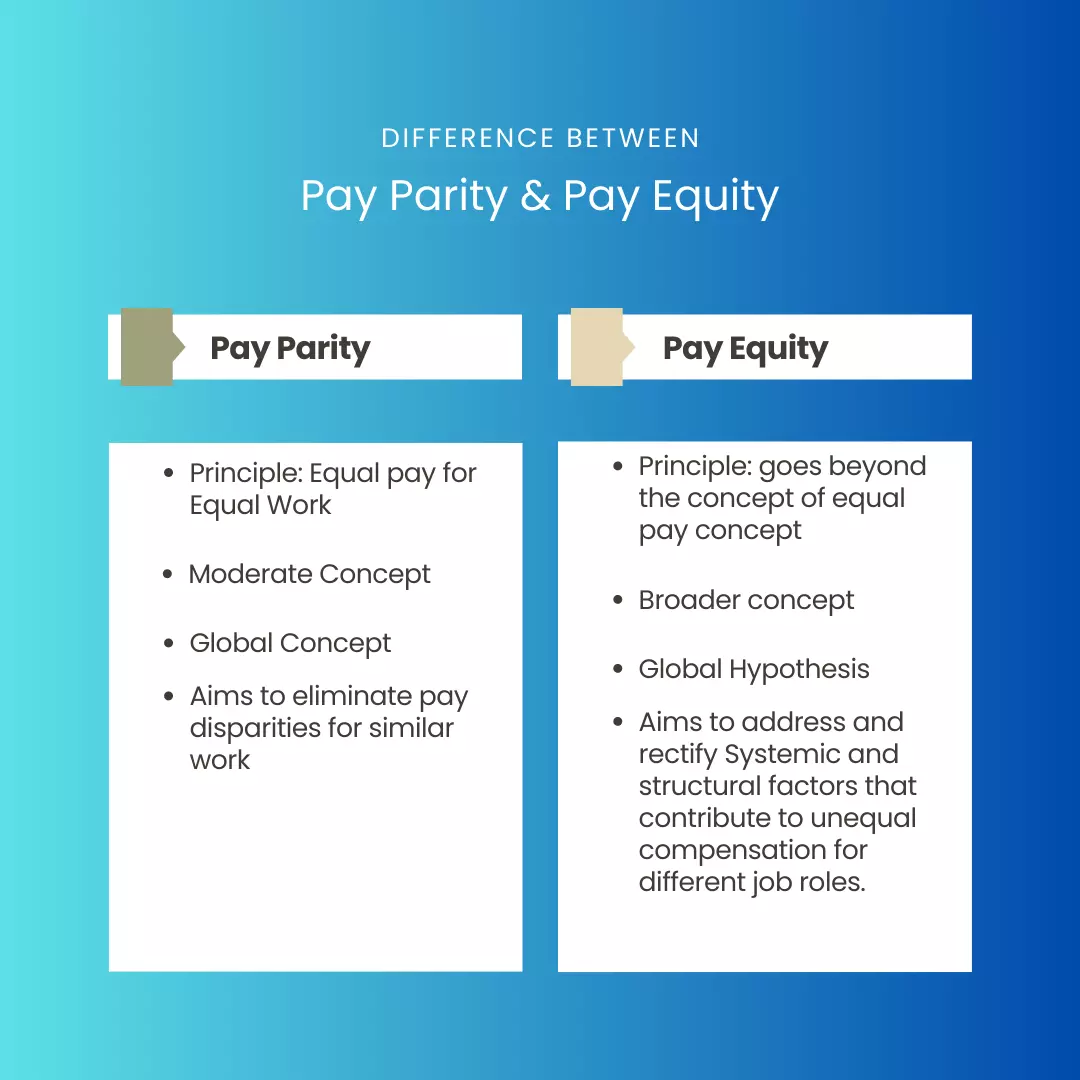
Pay parity vs. Pay equity
What is The Equal Remuneration Act 1976?
The Equal remuneration act 1976 denotes and ensures equal pay for equal work for both men and women as well as prohibits employers to discriminate against women in respect of wages paid, promotion practices, compensation, and other benefits.
The key elements of The Act include:
- Equal remuneration for equal work
- Provides complaints mechanism in case of discrimination in terms of remuneration.
- Establishment of authorities to monitor and inspect equal pay for equal work provision.
- It ensures women have equal rights in the account of employment, recruitment, promotion, training, or transfer.
- Defines “work of equal value”, which means works that require equal skill, knowledge, responsibility, and efforts with the same working condition
- Establishment of a Remuneration Committee to advise employers of wage-related matters and ensure compliance with the Act.
- The Act requires employers to maintain and submit periodic wage reports to maintain transparency in remuneration paid to men and women employees.
- Aims to achieve pay parity hence achieving gender parity.
Laws prohibiting disparity in pay in India
There are a bunch of laws that prohibit disparity in pay and promote pay parity, such as:
- The Equal Remuneration Act of 1976
- Minimum Wages Act, 1948
- Equal work for Equal pay Principle- Though it’s not a specific law yet it is been recognized by Indian Judiciary
- Industrial Employment (Standing Orders) Act, 1946
- Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
Also Read:
Conclusion
Pay parity is a crucial as well as vital aspect which should be combatted. By this we can create fair workplaces, with inclusivity, support, and diversity in the workforce, ultimately leading to greater gender equality and social progress. Hence creating a healthy and productive work environment that contributes to the global economy as a whole.