A leave policy is an essential part of HR management. Employers must be aware of leave policies when they organize leave for employees. A proper balance should be struck between paid, non-paid, and national holidays.
Besides, arranging leave types assists employers in transparency during onboarding, as many candidates ask about the leave policy. A clarified leave policy maintains the company’s commitment to employee well-being and cultivates a culture of trust, inclusivity, and mutual respect.
Different policies or national and state laws exist regarding the selection of leave count for a particular year. The Factories Act of 1948 enacts laws the Indian Factory Act. For other establishments like IT/ service companies, shops, etc., the policies are determined under the Shops & Commercial Establishments Act.
Apart from the mandatory leave types, companies provide several other essential ones.
This blog will highlight India’s different types of leave, followed by those of other states. Moreover, what kinds of leaves do the government and other employees receive?
Types of Leave in India
Here is a list of different types of leave the company plans for a fiscal or calendar year. Employees can use the leave management system to apply for leave on or before the due date.
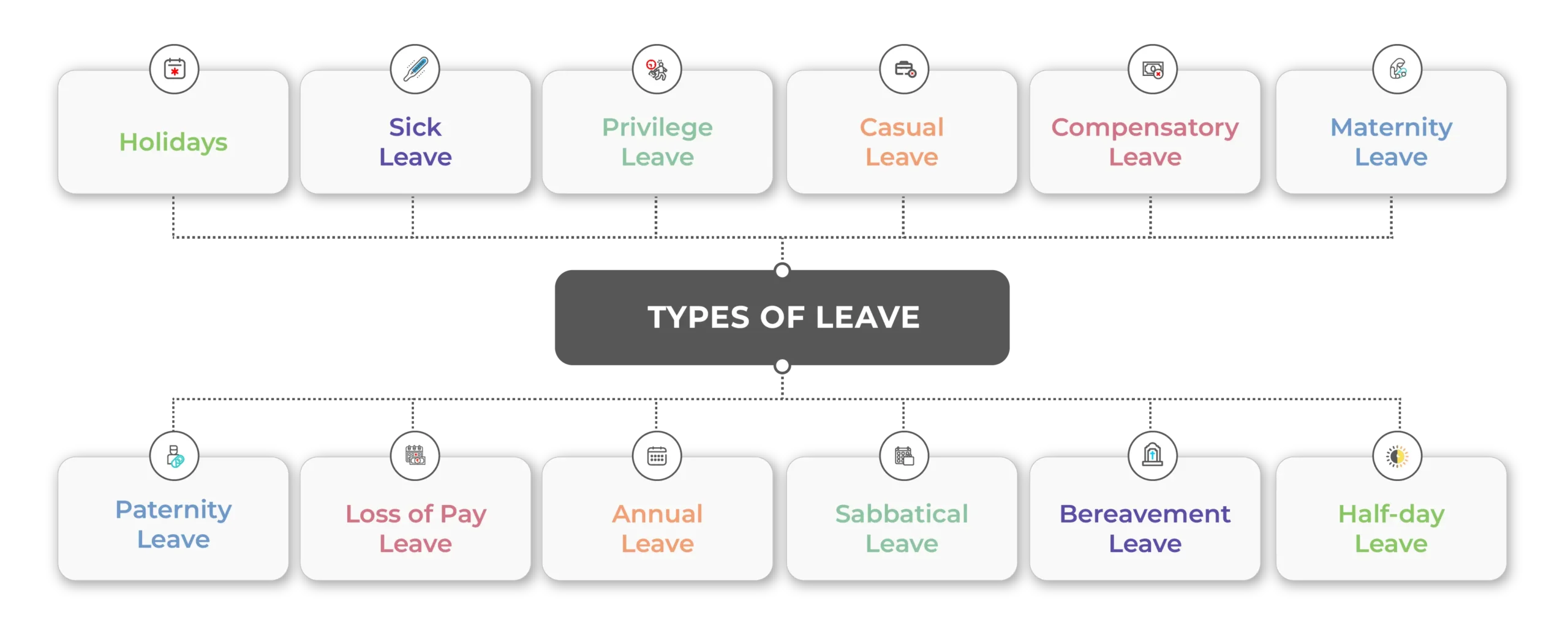
1. Holidays
‘Holiday’ is one of the company’s mandatory leave counts, which companies must follow. It includes national or regional based big festivals and other government holidays, etc. It is also popularly known as a public holiday.
All government companies and most public and private entities arrange public holidays for employees. These mainly include Independence Day, Holi, Dussehra, Republic Day or any announced date in memory of the death or birth of renowned people in India. Mandated holidays are one type of Leave for employees in India.
2. Sick Leave
Sick Leave is the next mandatory leave type that an employee expects from the company. It is used when employees feel ill and take time off. This leave provides sick employees time to recover completely before rejoining.
However, whether or not a particular organisation provides such Leave depends on that organisation. With the provision of SL, employees need not worry about their pay cut, as they are paid for the homestay. The company itself sets the number of Leave or Sick Leave. It can be anywhere around 10-15 per year.
3. Privilege Leave
The definition of the leave type is the same as its name. In this leave type, the employees get privileged by receiving leaves as their claim. The company mainly rewards employees with this paid Leave (PL).
The leaves can be around 20-22 per year, depending on companies and their HR. These are the days when employees can take a day off and enjoy themselves without losing pay. Thus, the name paid Leave is earned Leave. Employees only need to get the Leave approved by the manager to take advantage of it.
4. Casual Leave
Casual Leave is another essential type in which employees take a day or days off for personal reasons or without a cause, unlike paid Leave.
The primary reason for such leaves is religious Leave, like Eid and other minority festivals. Employees here enjoy paid Leave for the day. The number of casual leaves per year is around 3 to 5, which can neither be encashed nor carried over to the following year. This is highly dependent on the manager’s approval.
5. Compensatory Leave
Compensatory Leave is available for companies where HR performs overtime management. Companies often pay extra and provide a day off to employees who work overtime. It is a paid Leave received by sales or marketing employees or upper-level management.
This leave calculation concerns worked hours at the workplace. Extra or fewer hours can be compensated with pay later during payroll, helping maintain smooth leave management and flexible working.
6. Maternity Leave
A company must ensure that this type of Leave is included in its policy. This type of Leave is only for female employees who will give birth to a baby or who have to take care of a newborn baby. The leaves ensure that the women employees get a chance to recover from pregnancy. The tenure extends from 6 months to 1 year for full recovery.
However, it depends upon the country and location of the company to get the policy.
7. Paternity Leave
Such leaves are not mandated by law and employment rules. While some companies practice a couple of weeks of paternity leave for men or fathers, a new father or caretaker of a child can take this type of Leave without worrying about his pay loss.
It is specially meant to assist a mother in nurturing their newborn baby after delivery. Most companies do not observe paternity leave on a vast scale, but some do.
8. LOP day (Loss of Pay Day)
And here comes the loss of paydays. Employees take these leaves after fully redeeming their Paid leaves. Generally, each LOP day has a 40 per cent cut on per-day income.
There are no restrictions on taking leave for loss of pay, though there are often very few rules. Companies must make their leave policies very clear on day 1.
9. Annual Leave
Annual Leave is a type of leave where employees get time off at the end of the fiscal year or annual year to rest from work. It is mainly known as a benefit package or reward for the employee, where they take a week off or some days off and invest their time to travel, tours or households while still receiving their regular salary. The annual leave amount depends on the length of their employment, the company’s policies, and the laws in their country or region.
Annual Leave can be used for vacations, personal time, or family events. Some companies allow employees to carry over unused leave to the next year, while others may require employees to use their leave within a specific time frame or lose it.
10. Sabbatical Leave
It is certain kinds of leave where employers give employees time to upskill, sharpen their knowledge, and prepare for their upcoming projects. Employees mainly need the sabbatical leave to improve their learning and help in future operations.
Employees mainly take leaves for education advancement, career breaks, career upbuilding, etc. There is no legal provision around these based on the sabbatical leave, and since it is not approved immediately, employees need to plan for them.
11. Bereavement Leave
Due to some unfortunate event like the demise of a family member, employees take time off, known as bereavement leave. There is no labour law or policies based on bereavement leave. Many companies ensure this kind of leaves on the ground of compassion.
12. Half-day Leave
Half-day leave, a frequently utilized leave type, allows employees to manage personal tasks such as doctor’s appointments, financial work, or other essential chores without sacrificing the entire workday. This flexibility promotes a healthy work-life balance and ensures employees are more productive and engaged during working hours.
State-Specific Different Types of Leave in India
Here is a detailed overview of state-specific different leave types in India.
| Sl. No. | Act | Type of leave | Entitlement | No. of leaves | Carry Forward |
| 1 | Factories Act, 1948 | Earned Leave | Completing 240 days work | One leave for every 20 days work | 30 days |
| 2 | West Bengal Shops and Establishment Act | Earned
Leave |
A year of work | 14 days | 28 days |
| Sick Leave | From joining date | 14 days (Half pay) | 56 days | ||
| Casual Leave | From joining date | 10 days | Cannot be accumulated | ||
| 3 | Bihar Shops & Establishment Act
And Jharkhand S&E Act |
Earned Leave | 240 work days the previous year | One leave for 20 days of working | 45 days |
| Sick Leave | From joining date | 12 days (Half pay) | NA | ||
| Casual Leave | From joining date | 12 days | NA | ||
| 5 | Delhi S&E Act | Privilege Leave | 5 days for every 4 months for permanent employees | 15 days | 45 days |
| Sick Leave/ Casual Leave | 1 day for every 1 month of employment | 12 days | NA | ||
| 6 | Andhra Pradesh S&E Act | Privilege Leave | Completing 240 days work | 15 days | 60 days |
| Sick Leave | 1 day for every 1 month of employment | 12 days | |||
| Casual Leave | 1 day for every 1 month of employment | 12 days | |||
| Special Casual Leave | Once after completing 2 years in service | 6 days | NA | ||
| 7 | Karnataka S&E Act | Earned Leave | 240 work days the previous year | 1 every 20 work days | 30 days |
| 240 work days the previous year | 1 every 20 work days | 40 days | |||
| Sick Leave | From joining date | 12 days | |||
| 8 | Kerala S&E Act | Annual Leave | After complete a year in service | 12 days | 24 days |
| Sick Leave | From the joining date | 12 days | NA | ||
| Casual Leave | From the joining date | 12 days | NA | ||
| Special Casual Leave | After an operation or surgery | 6 days for men and 14 days for females | NA | ||
| 9 | Bombay S&E Act | Annual Leave | 240 work days the previous year | 21 days for every 60 days of work | 42 days |
| 10 | Orissa S&E Act | Annual Leave | 240 work days the previous year | For Adult:- 1 day for every 20 days worked For Child:- 1 day for every 15 days worked |
30 days for adults and 40 days for child |
| Sick Leave | From joining date | 15 days | NA | ||
| 11 | Rajasthan S&E Act | Annual Leave | 240 work days the previous year | For Adult:- 1 day for every 12 days worked For Child:- 1 day for every 15 days worked |
30 days for adult and 40 days for child |
| 12 | Tamil Nadu S&E Act | Privilege Leave | A year in service | One every month | 24 days |
| Sick Leave | Join Date | 12 days | NA | ||
| Casual Leave | Join Date | 12 days | NA | ||
| 13 | Uttar Pradesh S&E Act | Earned Leave | A year in service | 15 days | 45 days |
| Sick Leave | After six months in service | 15 days | NA | ||
| Casual Leave | After 6 months in service | 10 days | NA | ||
| 14 | Punjab S&E Act | Earned Leave | After 20 days of continuous employment | One in 20 days | 30 days |
| Sick Leave | Joining date | 7 days | NA | ||
| Casual Leave | Joining Date | 7 days | NA |
Why Is Leave Policy Important in Every Company?
In every company, employers face challenges and have to work on leave counts before announcing leave status for a fiscal year over the leave management system. What is the precise importance of the different leave types in an organization? Or should we distribute the types of leave to the employees? Let’s explore.
1. Importance of Annual Leave (Paid Time Off – PTO)
➔ Employee Well-being
Annual leaves allow employees to care for their mental and physical health, ensure they get recharged, and reduce stress. A certain amount of annual leave helps employees be more productive and motivated.
➔ Attraction & Retention
A generous annual leave policy attracts employees during onboarding. They feel satisfied and happy when they have time to take vacations or attend to personal matters.
➔ Compliance
Many companies have boundaries regarding the minimum amount of paid leave in their time off policy. So, having satisfactory annual leave makes the employees happy and stay positive during their entire working tenure. It enhances company productivity and business expansion.
2. Importance of Unpaid Leave
➔ Flexibility
Though unpaid leave is not always a satisfactory option, it often provides flexibility when employees need to take a leave without a paid one. Employees use their HRMS software and related tools, such as attendance management software, to count their daily hours while maintaining flexibility.
➔ Cost Management
Companies often offer unpaid leave to employees when they have a certain cost management plan. For example, some companies provide unpaid leave to female employees during their maternity leave.
3. Sick Leave Importance
➔ Employee Health
Sick leave ensures employees take time off when they are ill without worrying about their financial stability or working behaviour.
➔ Enhanced Productivity
When an employee falls ill, productivity itself diminishes. So, sick leave helps the employees get better without any financial loss. Moreover, it helps to prevent the spread of illness to co-workers, helping maintain a healthier and more productive workplace.
4. Parental Leave (Maternity/Paternity Leave) Importance
➔ Support for Parents
Parental leaves support both parents in caring for their newborn, looking after themselves, and adjusting to their new role without the financial pressure of losing income.
➔ Gender Equality
Parental leave ensures gender equality by offering equal leave opportunities to all genders.
5. Importance of Bereavement Leave
➔Support During Grief
A relationship is formed between employees and employers during an entire employment tenure. By arranging bereavement leave, employers show empathy for the employees’ loss and support them by giving them the space to grieve and attend to personal matters without work pressure.
6. Importance of Personal Leave
➔ Flexibility for Employees
Personal Leave allows employees to take time off for any personal reason. Even here, they haven’t shared the reason behind taking the leave. It can be attending to personal matters, family issues, or other life events. This flexible time off can improve job satisfaction.
➔ Work-Life Balance
Personal Leave helps employees maintain work-life balance by improving their happiness and productivity.
7. Importance of Public Holidays Leave
➔ Celebration
A national holiday is essential to celebrate a national or religious event. On this day, employees spend quality time by participating in these occasions, promoting a sense of well-being and belonging.
Types of Leave for Government Employees in India
Government employees in India may get some extra privileges in case of time off in a fiscal. Here are some of the key leaves available:
➔ Earned Leave
Government employees accrue 2.5 days of leave in a complete month of service and receive 300 days of leave encashment at retirement.
➔ Half-Pay Leave
Government employees receive 20 half-day leave in the fiscal year, which can be converted to 10 full days.
➔ Commuted Leave
An employee’s total leave balance can be converted to double half-pay leaves within the same duration.
➔ No due leave
Government employees can avail of 360 days of advance leave in case no leaves are available for a particular fiscal.
➔ Maternity Leave
180 days of paid leave available for government employees.
➔ Paternity Leave
Fifteen days of paternity leave are available for employees who have just become fathers.
➔ Childcare Leave
Female employees receive 730 leave days to care for their children.
➔ Sabbatical Leave
Employees receive leave to enhance their knowledge of specialized work or before taking on a considerable responsibility.
➔ Vacation Leave
Employees are entitled to one month of vacation leave in every fiscal.
FAQs on Types of leave
1. What are PL and CL leave?
PL, or Privilege leave, is a type of earned leave granted to employees who have worked for the organization for a long time.
CL, or casual leave, is given to employees when they can inform the company about a sudden leave due to unforeseen circumstances. The company provides CL when an employee takes leave for personal reasons but not for sickness or vacation.
2. How many Leaves are in a year?
According to the Factories Act, a single earned leave is granted for every 20 working days, or 18 leaves per year.
However, per the Shop and Establishment Act, only five privileged leaves are granted for four months of working days, i.e., 15 leaves in a year. This rule is granted as a minimum mandatory leave count irrespective of any workers.
3. What is DL Leave?
DL means Duty leave. Using this leave type, employees can take time off from regular work and perform any specific tasks like,
- Attending Client meeting
- Organizing Work Event
- Managing trips to carry out assigned duties, etc.
4. What is the Type of Casual Leave?
Casual Leave is short time leave taken by the employees. It is categorised between;
- Short Duration: Typically 1-3 days at a time.
- Unplanned: For unforeseen personal or family emergencies.
- Limited Days: Set number of days per year.
- Paid Leave: Usually paid leave.









