Minimum Wages in India
Minimum Wages for States Across India
What are Minimum Wages in India?
A Minimum wage is the lowest legally mandated amount of compensation that an employer must pay to their employees for their labor. The Minimum Wage Act in India is a statute of rules prohibiting employers from paying less than a defined amount set by the government.
Every state government and central government has control over the building and rebuilding of minimum wage rules. The wage rate can be different based on numerous factors like working conditions, economic factors, living standards, cost of living, nature of work, etc.
The unorganized sectors receive variable dearness allowance (VDA) during fluctuation of the consumer price index. Subsequently, the workers receive the daily minimum wages are combined with a VDA, announced by their state government.
The minimum wage is revised by the central and state governments every five years. At present, the minimum average wage rate in India is Rs 176/day for an eight-hour workday.
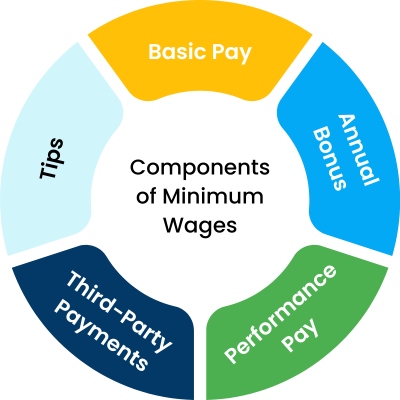
What are the components of Minimum Wages?
A minimum wage includes the base salary and allowances. Allowances like the shift pay, performance pay are considered as minimum wages, where as the overtime working payments, extra work payment aren’t. Here’s the details of components of minimum wages are as following,
Minimum wage components consist of
- Basic Pay
- Annual bonus
- Performance Pay
- Incentives
- Third-Party Payments
- Tips
Components not included
- Extra work payment
- Leave allowance
- Expense Allowances
- Profit
- Overtime payment
- Special Payments
How is the minimum wage calculated in India?
India’s minimum wage structure is based on factors like industry, occupation, skill level, development level, industry, etc. The Indian government offers a competitive minimum wage of around ₹178 per day, which amounts to ₹5340 per month. It is important to note that the mentioned amount is the base-level amount. The wage rate will vary depending on the geographical areas and other criteria.
Every State Government can fix the minimum wage rates based on a few parameters.
- Nature of employment
- Industry
- Work Types
- Geographic location
- Employee’s age
